Antibiotic Allergy Testing Kit
Antibiotic Allergy Testing Kit
The antibiotic allergy testing kits have been widely used in major hospitals and private clinics for the diagnosis of Penicillin, Amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid allergies in Australia and New Zealand for over ten years.
ALLERGENIC DETERMINANTS DESCRIPTION
Main allergenic determinants implicated in type I or immediate hypersensitivity to Amoxicillin and related antibiotics (amino penicillins), dosed and stabilized by means of freeze-drying. To be exclusively used for the diagnosis of type I or immediate hypersensitivity to amino penicillins and related antibiotics (amino penicillins) by means of skin test (skin prick test and intradermal reaction).
PENICILLIN
Penicillin Allergenic Determinants are classified and labelled as: - Major Determinant Benzylpenicilloyl poly-L-lysine (PPL): formed by the bonding of the primary determinant of benzylpenicillin and related antibiotics (beta-lactam) to lysine chains. - Minor Determinant Mix (MDM): formed by Sodium benzylpenicillin, Benzylpenicilloic acid, and Sodium benzylpenicilloate, which are involved in the sensitisation to benzylpenicillin and related antibiotics (beta-lactam).
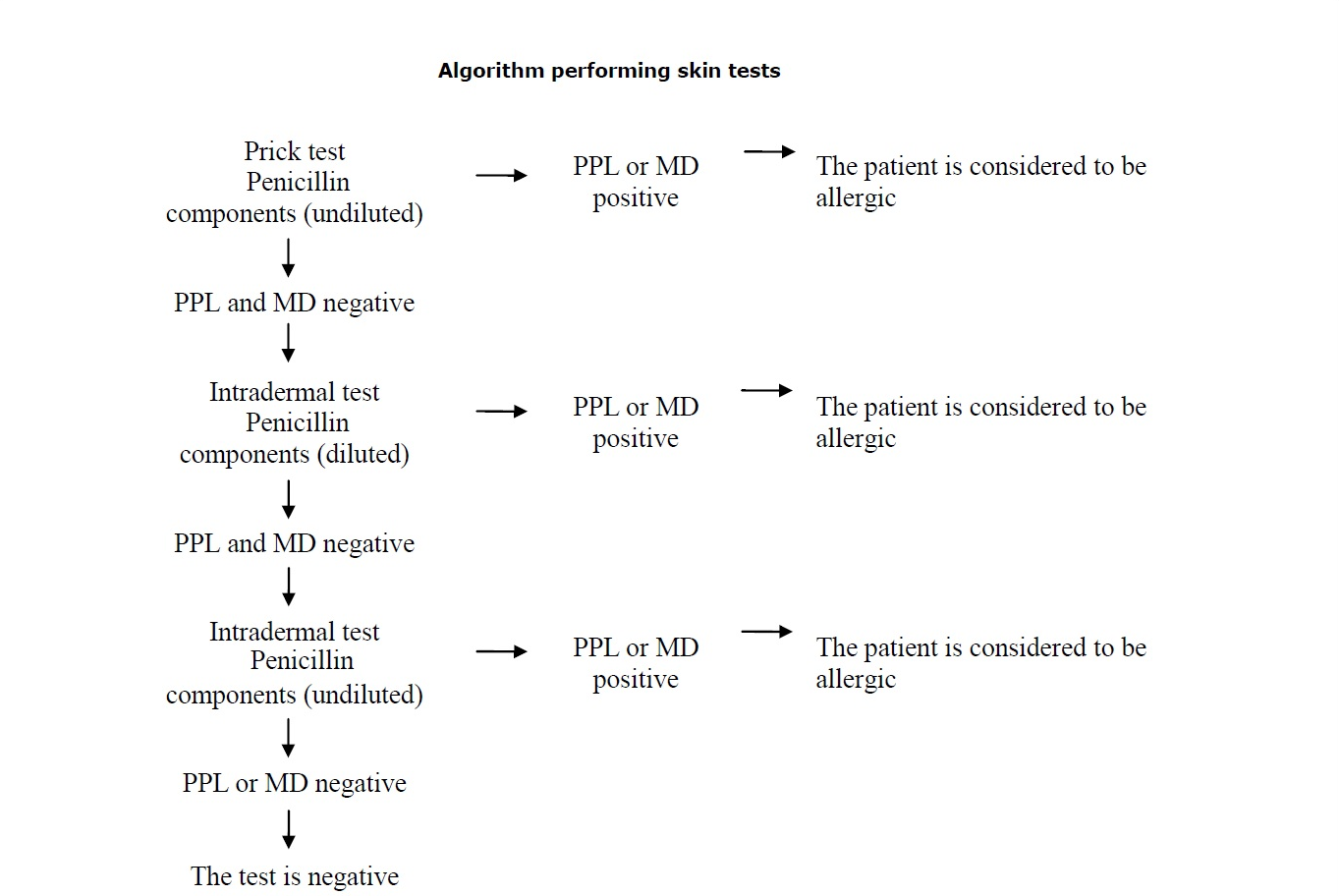
Cutaneous tests must begin by studying cutaneous reactivity to the Major Determinant (PPL). The minor determinant mix (MDM) should only be used when the result of the cutaneous test using the Major Determinant (PPL) has been negative. Cutaneous tests must always start with the prick test technique. Intradermal tests should be used only when the prick tests are negative. As a preventive measure, it is advisable to apply a set of dilutions, at a ratio of 1:100 and 1:10, prior to starting the Major Determinant (PPL) and/or the minor determinant mix (MDM) intradermal tests. In patients with symptoms compatible with a severe reaction, or with a high risk, the dilutions for the cutaneous tests should begin at 1:1,000.
In cutaneous tests, it is advisable to follow the algorithm for the study of sensitivity to penicillin determinants shown below:
AMOXICILLIN
Skin testing with Amoxicillin should be started by assessing the skin reactivity by the skin prick test technique. The use of intradermal testing should only be started when skin prick tests have yielded negative results.
Skin testing should always be started with skin prick test with Amoxicillin. Before performing intradermal testing, preventively, it is recommended to start with the application of a dilution panel, 1:100 and 1:10.
In high-risk patients or patients with symptoms suggestive of a severe reaction, dilutions for skin testing should be started with the 1:1000 dilution.
The following algorithm for assessing the sensitivity to amoxicillin and related antibiotics (amino penicillins) is recommended when using skin testing:

CLAVULANIC
Clavulanic is a medicine containing potassium clavulanate which is isolated and stabilised by lyophilisation. It is presented with a reconstitution diluent to obtain a suspension for administration by scarification and/or the intradermal route.
Clavulanic is used exclusively for the diagnosis of type I (or immediate) hypersensitivity to potassium clavulanate, by means of skin tests (prick and/or intradermal tests).
For skin testing, it is recommended to start the Intradermal Test at the lowest concentration and then follow this algorithm:
