Polymerized Subcutaneous
Phleum pratense - native extract
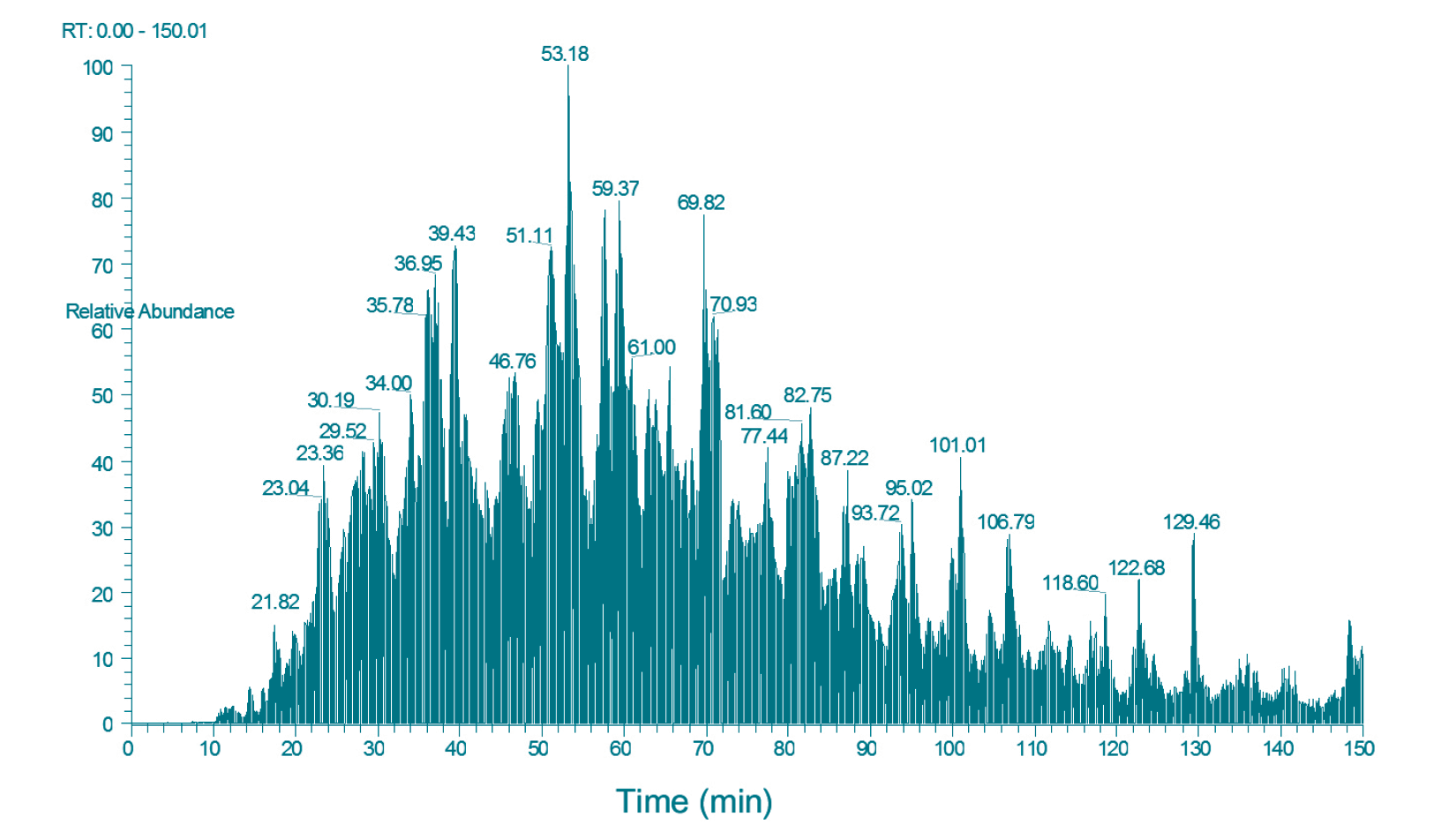
By means of chromatography (nano-HPLC) and mass spectrometry, the proteins present in the native and polymerized extracts are separated and subsequently identified.
Phleum pratense - polymerized extract
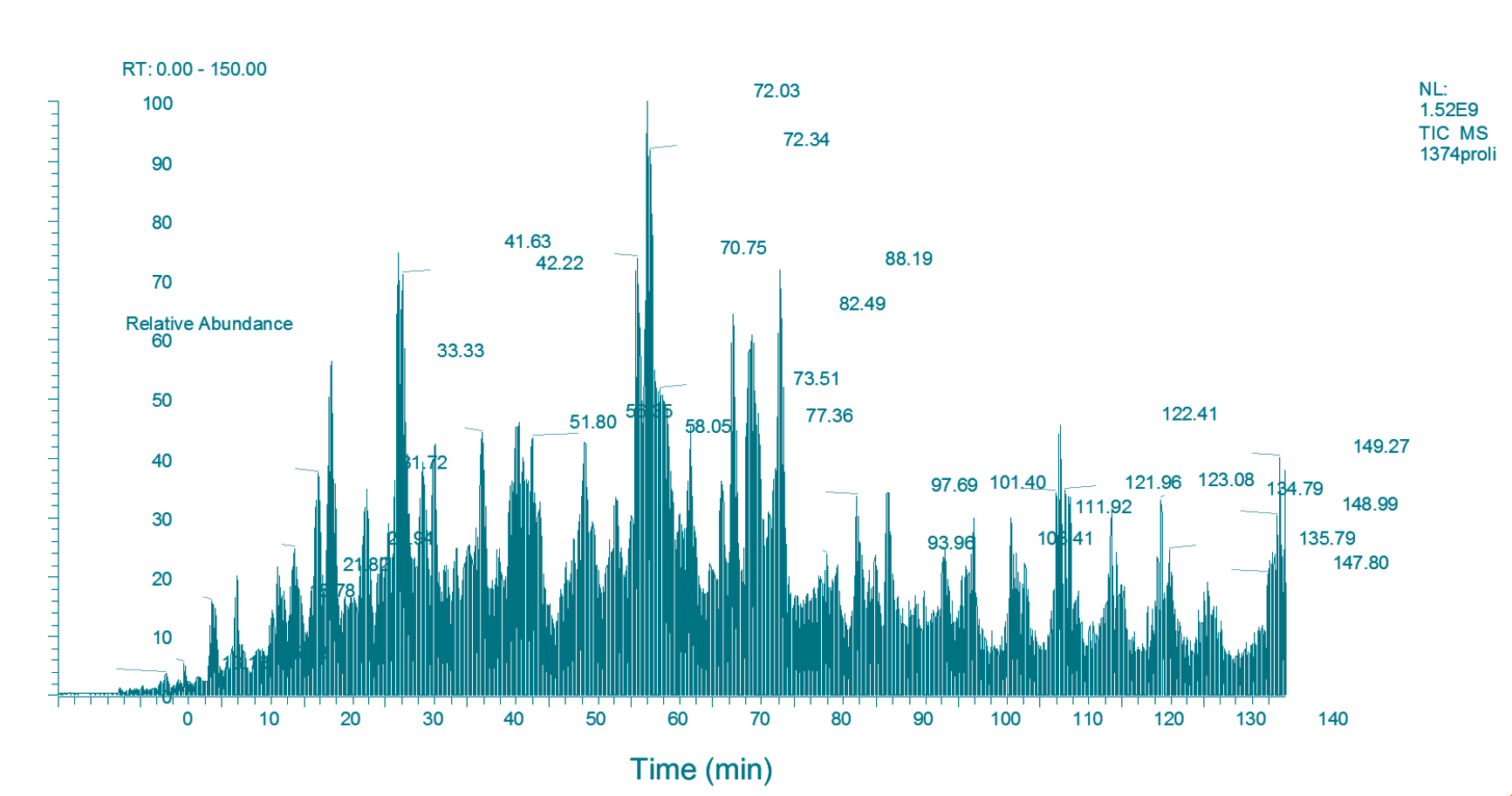
The polymerized extract of Phleum presents the same allergens, with their isoforms, as the native extract.
Titration of IgG antibodies against Phleum pratense
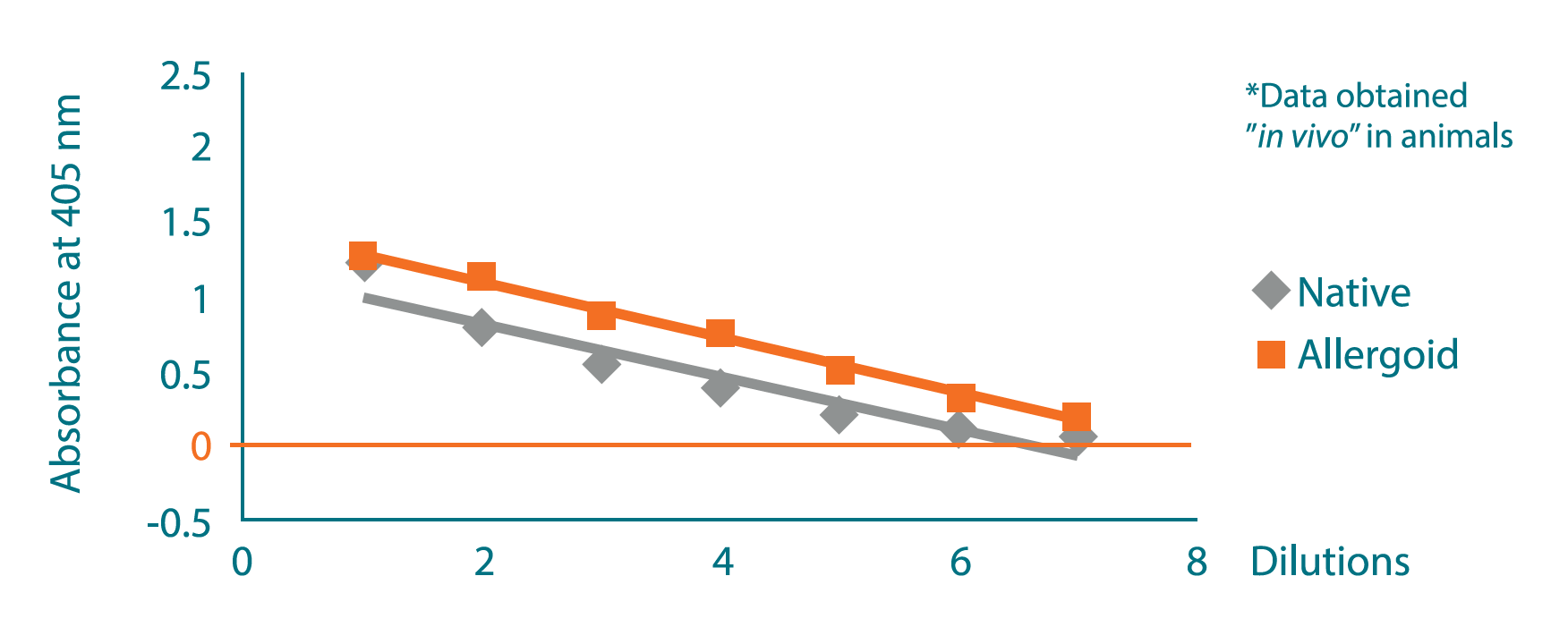
Animal model in rabbits to check the immunogenic character of a polymerized extract of Phleum pratense.
The immunogenic profile of a polymerized extract of Phleum pratense is similar to that of a native extract of Phleum.
Antigenogram and Allergogram
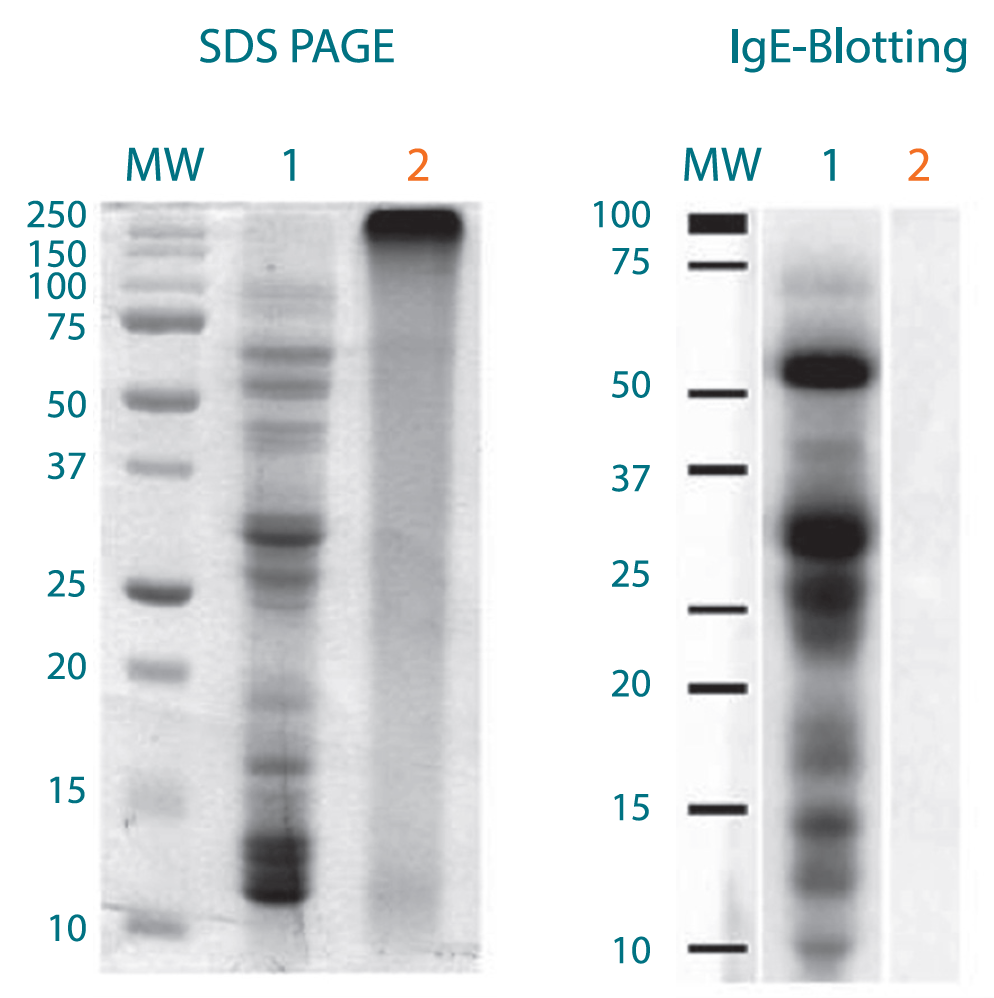
Molecular Weight Pattern
1. Native extract of Phleum pratense
2. Polymerized extract of Phleum pratense
SDS Page:
Native extract of Phleum pratense – reveals all allergens described for this species
Polymerized extract of Phleum pratense – no proteins between 10-250 kDa found
Immunoblotting:
Serum of patients sensitised to Phleum pratense mostly recognise Phl p 1, 4 and 5 allergens of native extract, but do not recognise polymerized extract
Reduced allergenicity of polymerized extract
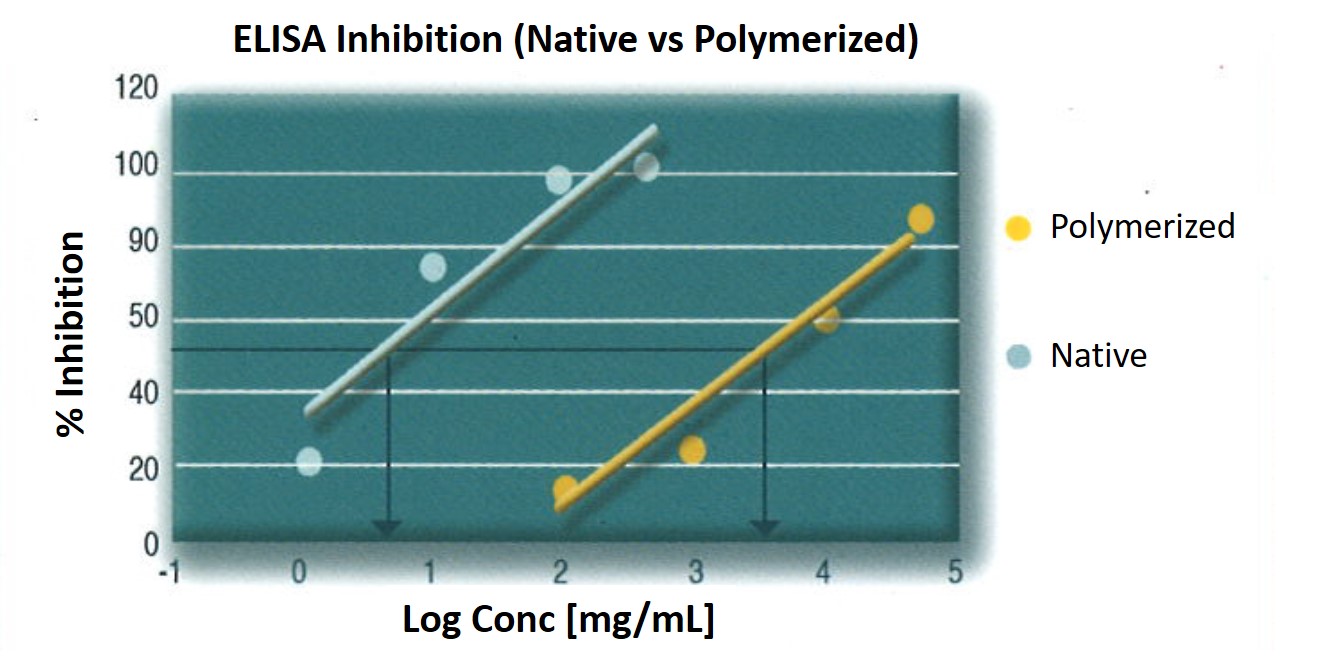
ELISA inhibition of a native extract in the solid phase and native and polymerized extracts as inhibitors.
The IgE binding capacity of a polymerized extract is much lower than the IgE binding capacity of a native extract.
Grass Pollens
Cynodon dactylon
Wild grasses (Lolium, Poa, Phleum, Dactylis)
Lolium perenne
Weed Pollens
Artemisia vulgaris
Chenopodium album
Parietaria judaica
Plantago lanceolata
Salsola kali
Tree Pollens
Cupressus arizonica
Olea europaea
Platanus acerifolia
Mites
Blomia tropicalis
Dermatophagoides farinae
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
Lepidoglyphus destructor
Mite Mixture
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
Dermatophagoides farinae
Lepidoglyphus destructor
Blomia tropicalis
Pollen Mixture
Wild grasses
Olea europaea
Cupressus arizonica
Parietaria judaica
Salsola kali